Forests are an essential part of Earth’s life cycle Cover approximately 31% of the planet’s total land area. However, there are more than 75% of the surface of the planetsHuman activities, such as deforestation, have altered and degraded the environment. Deforestation alters weather patterns and destroys habitats, livelihoods, and food security in rural communities. It also causes irreversible damage and destruction to entire ecosystems. How does deforestation impact the environment and what are the threats it poses for living species?
It is important to understand why forests are essential for human survival in order to answer the question “How does deforestation affect the environment?” Deforestation is the deliberate clearing of forest land for another purpose. One of the most important is deforestation. Main reasonsThis destructive practice is caused by agricultural expansion and cattle rearing. Studies have shown that Each year, 15,3 million trees are felledNearly half of the world’s trees have been cut down by humans in the last 12,000 year. This practice is dangerous for the environment. It alters the climate and different ecosystems and threatens the existence millions of people and animals.
Climate Change and the Effects of Deforestation
The scientific consensus regarding deforestation is that this accelerates climate change at an alarming rate. Global Forest Watch made this clear: Protecting tropical rainforests is vitalFor achieving the climate goals set out in the Paris Agreement. Trees are well-known for their ability to absorb carbon dioxide via photosynthesis. Healthy forests are extremely valuable carbon sinks. The Amazon rainforest is one of the most important. However, These sinks are being transformed by deforestation into huge net emittersThis could have major implications for slowing down climate change and contributing significantly to an increase in global temperatures. The current rate of rainforest-loss-generated emissions is nearly 25% higher that those in the European Union and slightly below US levels. Humans burning vegetation also increases the risk for wildfires. This in turn contributes to forest destruction and intensifies deforestation.
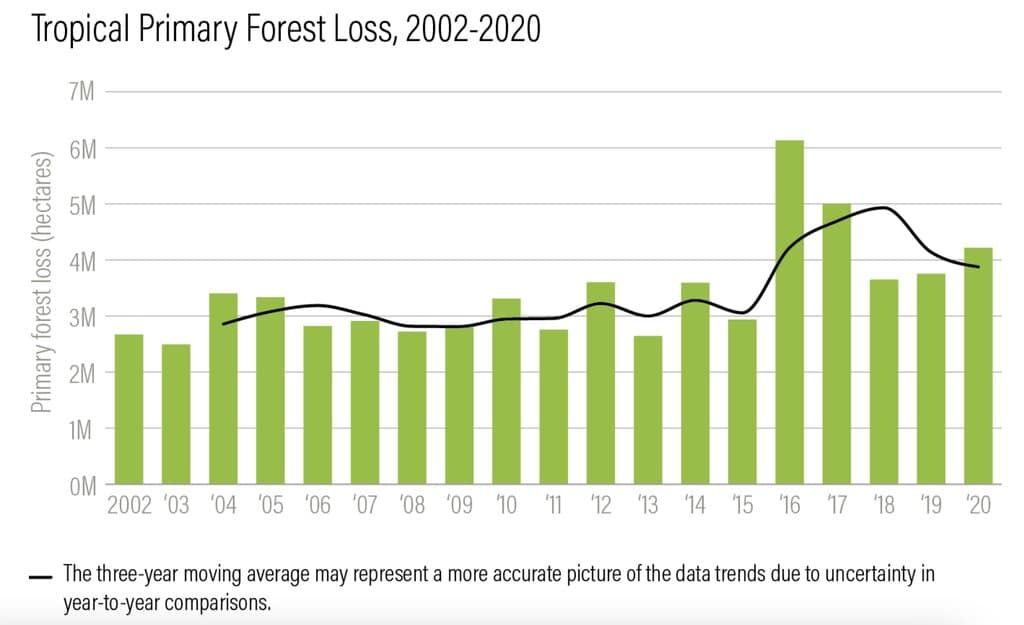
Figure 1: The loss of tropical primary forest between 2002-2020. Image by Global Forest Watch
The Water Cycle and Soil Pollution: The Impact of Deforestation
Forests are not only carbon sinks but also play an important role in the water cycle and serve the vital function of preventing desertification. Reduced precipitation can cause disruption to the water cycle, resulting in a decrease in river flow and increased water volume. Research has shown that the Amazon rainforest is a good example of this. At least 80% of its treesTo keep the hydrological cycle running, it would be necessary to create new forests. The Amazon is currently at 17% forest loss. Its tipping point. Statistics show that tropical deforestation is on the rise. Amazon Rainfall is reduced by approximately 10%Each year, the average rainfall is 138 millimeter. The South Asian Monsoon region has a much lower rainfall, with approximately 138 millimeter. India receives 18% less rainfallIn one year.
Trees, in addition to their contribution to water flow, help the land retain water. They also provide rich nutrients that sustain forest life. Deforestation exposes the soil to wind and rain, leaving it without cover. This leaves soil open to erosion and makes it more susceptible to being washed away. According to the World Wildlife Fund, as much as Half of the world’s topsoil was lostBecause of the loss of nearly 4 million acres of forest since the turn of the 20th Century,
Humans and Deforestation: The Impacts
Answering the question “How does deforestation affect the environment?” you might discover that it has an impact on the human population. The destruction of entire forests and trees is also causing the destruction of homelands. Deforestation has devastating effects on indigenous communities that live in forests and rely on them for their survival. These tribes are forced to leave their homes and to seek other means of support as their resources and houses are destroyed. The Amazon rainforest is the home of Over one million Indigenous peopleMost of them are Indian-born and have been divided into over 400 indigenous tribes. They live in settled villages along the rivers and harvest and hunt their food. These uncontacted tribes follow the rules of nature, but they are becoming increasingly vulnerable due to deforestation. Many of them have had to migrate. Some tribes move into areas that are occupied by other tribes and strain the lands resources. Others have to relocate to urban settings and change their lifestyle.
Deforestation has an impact on animals and plants
Animals are also among the most affected by deforestation, along with Indigenous tribes. More than a million species live in forests around the globe. 80% of all terrestrial insect, plant and animal species. The rapid destruction of forests is causing a decline in biodiversity that has never been seen before. Deforestation is the main cause of habitat loss for animals and plants. Many factors, including the removal of trees, can lead to species extinction. Land erosion causes soil to lose its nutrients, which are vital for both animals as well as plants. Many animal species are dependent on certain plants and their fruits as food sources. These resources are often lost and animals can become weaker, more susceptible to diseases, and eventually starve.Another important function of trees is to maintain constant temperatures in their forests. Temperature can fluctuate more from day to night when deforestation is occurring, and this can often prove fatal to many animal species.
The Effects of Deforestation and Food Security
Another major effect of deforestation on food security is the loss of biodiversity. Deforestation reduces food availability for Indigenous tribes, animals and plants that live in forests. However, it also has a significant impact on weather patterns and soil degrading which can drastically reduce agricultural productivity. The trend is most detrimental to populations located near tropical forests. Millions of people who live in these areas rely almost entirely on agriculture, making them extremely vulnerable to the effects of deforestation on food security. They are also struggling to grow enough food to prevent crop damage and to keep crops from being destroyed. It has been proven that Amazon deforestation contributes to the loss of biodiversity. Reduced pasture productivityAs well as 39%, Fall in soy yieldsNearly 25% in more than half of the Amazon region, and a staggering 60% within a third.
Solutions to Deforestation
How deforestation affectsThe environment can be impacted in many ways and it is critical that people take action to reduce its negative effects. Individually, you can reduce meat consumption, go paperless, recycle as much as possible, choose natural products that don’t contain palm oil, and support organisations and sustainable businesses that are committed to reducing the harmful practice. The government can reduce the negative effects of deforestation by introducing policies to protect natural forests, regulate mining and log operations, and other operations that involve the destruction or removal of tree plantations.