[ad_1]
Tornadoes Tore up homesNew Orleans and its suburbs were reported in communities TexasTo MississippiAnd AlabamaAs Severe stormsIn late March 2022, a tornado swept across the South. We asked tornado scientists Ernest AgeeExplain what causes tornadoes in the United States and how tornado activity has moved eastward from Tornado Alley in recent times.
What causes tornadoes
Tornadoes begin with thunderstorms. The thunderstorm is the parent of the tornado. Tornadoes can form when severe storms are possible in the atmosphere.
The ingredients for a tornado are low-level heat and humidity, cold air aloft, and a favorable wind field. The wind field must increase in speed with height as well as change in wind direction at lower levels.
A combination of wind, heat, and moisture can create rotating thunderstorms capable to spin off a tornado or its family. Thunderstorms capable to spinning off tornadoes often develop alongside and ahead of a thunderstorm. Frontal boundary – where warm and cold air masses meet – often accompanied above by a strong jet stream.
Why are tornadoes becoming more frequent? Climate change is a factor?
Studies do show tornadoes getting More frequent, more intense, and more likely to occur in swarms.
The strongest and longest-lasting tornadoes are those that are known as supercells – powerful rotating thunderstorms. The December 2021 tornadoes, more than 60The supercell that caused the storm to sweep across Kentucky and neighboring states was responsible for the tsunami. The Alabama’s 2011 outbreakAnother.
All this takes place under the global warming umbrella. While it’s still It is difficult for climate models to be assessedThey can even create a tornado from something as small as an egg. Project increases in severe weather.
What’s interesting is that despite that increase, the per capita death toll from tornadoes has In fact, the number of people who have been affected by this has droppedin the second half the past 100 years. As terrible as these new outbreaks may be, science and technology are saving lives faster than storms are killing people.
Scientists now have the ability to predict and forecast where tornadoes might occur. If you look at NOAA’s Storm Prediction Center website, you’ll see eight-day outlooks now. That’s based on scientific knowledge and technology able to target where conditions conducive to tornadoes are developing.
People also Know what to do nowThey are more likely to receive warnings and have more homes. SafeIt is able to withstand a tornado. Today, social media plays an important role. A few years ago, I had a student who was on his family’s farm when he got a text warning that a tornado was coming. His family was able to get to safety just before the tornado struck.
The Southeast is experiencing more severe storms. Has Tornado Alley shifted?
My students and I published the 2016 first paper that statistically clearly demonstrated the existence of the. The emergence of another center for tornado activityAlabama is the center of the Southeast.
Oklahoma still has tornadoes. The statistical center has since moved. Other research has been done since then. Similar shifts were found.
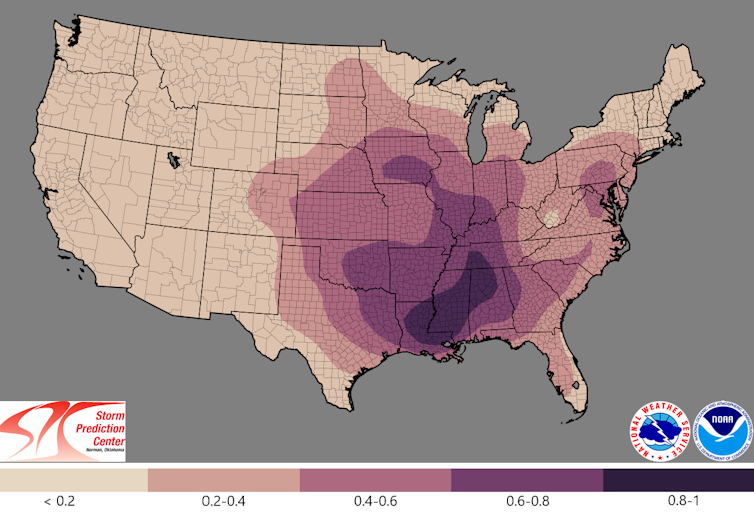
NOAA Storm Prediction Center
We observed a notable drop in the number and days of tornadoes in Tornado Alley in central plains. At the same time, we found an increase in tornado numbers in what’s been dubbed Dixie Alley, extending from Mississippi through Tennessee and Kentucky into southern Indiana.
The Great Plains’ dry air near the western boundary of Traditional Tornado Alley may be due to the fact that tornadoes are declining in Oklahoma, while wildfire risk is increasing.
Research by other scientists suggests that Dry lineThe difference between the wetter Eastern U.S.A and the dry Western U.S.A, historically around the 100th Meridian, has been Shifted eastwardBy About 140 milesSince the late 1800s. The dry line can be a boundary for convection – the rising of warm air and sinking of colder air that can fuel storms.
While scientists don’t have a full picture of the role climate change may be playing, we can certainly say we live in a warmer climate, and that a warming climate provides many of the ingredients for severe storms.
[Read The Conversation daily by subscribing to our newsletter.]
[ad_2]




