Tornadoes can be terrifying — whether you experience them or only see images of the aftermath.
Most tornadoes are short-lived and harmless. A tornado that is not normal and strikes humans can cause severe damage, even death.
This was what happened in the United States when a series tornadoes struck in early December. It left a trail of destruction that ran from Arkansas to Kentucky. Dozens of people were killed and many are still missing.
The US National Weather Service described one of the tornadoes as “potentially historic” — due to it possibly being on the ground for the longest distance on record.
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands are still without shelter
Struggling just to survive
A drone shot shows the extent to which destruction has occurred: Mayfield in Kentucky saw the water tower collapse like a house made of cards. “Our infrastructure has been so damaged. We don’t have running water. […]Our wastewater management system was destroyed, and there is no natural gas in the city. So we don’t have any other options,” Mayor Kathy Stewart O’Nan said to CBS. She added that many people were struggling for survival.
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands remain without shelter
Volunteers are available to help
Volunteers have volunteered at South Warren High School in Bowling Green to sort canned food and water. Kevin Kirby, a coroner, said that 11 people died in the same street of the town of about 70,000. He also stated that two infants were found among the bodies belonging to five relatives.
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands are still without shelter
Coping with loss and grief
Justin and Sunny, his girlfriend, took refuge in Wingo, Kentucky’s church-turned emergency shelter. Sunny’s brother died in the Mayfield explosion that killed at least eight workers.
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands remain without shelter
Many homes uninhabitable
Shelter organizers in Wingo want to create a mobile outdoor shower and laundry trolleys. They anticipate that many of those who are currently staying at the shelter will need a permanent place to live. Glynda Glover, 82, said that she would stay here until “any normal” is restored. “And I don’t even know what normal is anymore.” The wind blew through her apartment and covered it with asphalt and glass.
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands are still without shelter
Reconstruction can take years
At a mobile emergency center in Dawson Springs, Kentucky — another town devastated by the tornadoes — volunteers deliver drinking water. “It looks like an explosion. Jack Whitfield Jr., Hopkins County judge-executive, said that it was just “completely destroyed in areas.” He estimates that 60%, including hundreds, of the town’s homes, are “beyond repairs.”
-
After the US tornadoes, thousands are still without shelter
“It won’t always be the same”
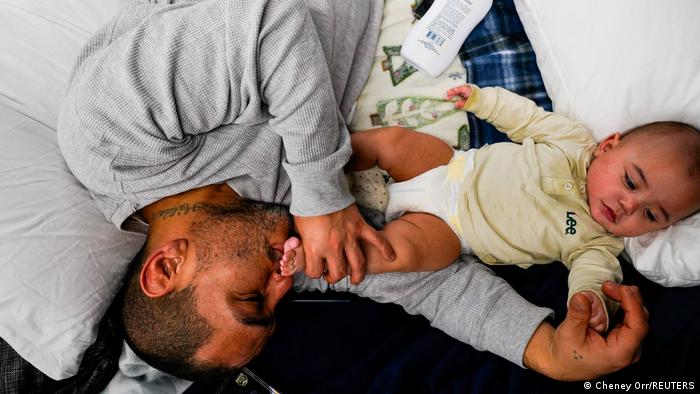
Anthony Vasquez, 42 years old, and his 4-month-old boy Michael, took shelter at the Wingo emergency shelter with about 100 others. Andy Beshear, Kentucky Governor, stated that “we’re not going let any of our family go homeless.” Cynthia Gargis (51), who was adopted by her daughter and works at shelter, doesn’t think “how we’ll ever overcome this.” It won’t be the exact same.
Author: Philipp Böll
How does a tornado form?
Scientists are aware of the basic ingredients that cause tornadoes but are still trying to figure out what causes them.
Walker Ashley, an atmospheric scientist from Northern Illinois University, said that “the truthful answers are we don’t know”.
Ashley is — what you might call — a storm chaser.
“I spend about a month out of the year chasing these weather phenomena, and they never want me to.” [turn into a tornado]Ashley said to DW that she is sitting down when Ashley is speaking.
Certain weather conditions
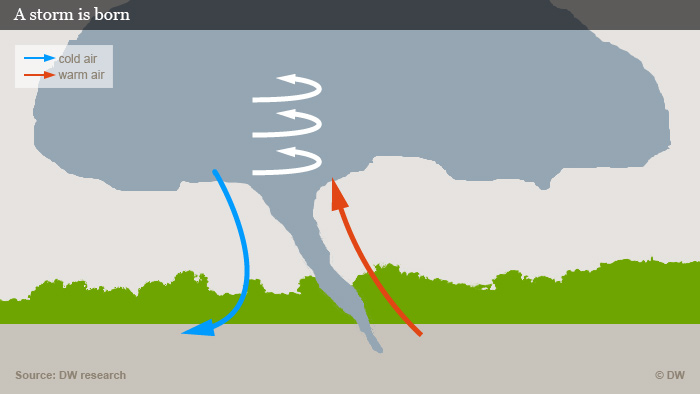
Tornadoes are formed in very specific weather conditions. A supercell is a rotating thunderstorm that causes tornadoes. A supercell can bring lightning and strong winds, hail and flash flooding.
If the wind speed or direction is different at different altitudes, then you can get a “wind shear.”
Although wind shears are usually harmless, they can cause air currents spin and create a horizontal tube out of air. This is a common phenomenon in supercell thunderstorms but it’s not yet a tornado.
Sometimes, a storm can suck up the tube of air until it becomes horizontal. It’s known as a mesocyclone when it happens.
This is still not a tornado. To form a tornado, there must be spinning air near to the ground.
The stronger the air tube rotates, the closer it can touch the ground. It is more likely to turn into a tornado. Ashley says: Think about it as a figure skater.
“When a figure skater extends their arms, they slow down.” Ashley says that figure skaters who bring their arms in accelerate. “And what a storm is does is it takes that same rotation, tilts the vertically and stretches them. It increases the rotation when it stretches it.
This causes warm air to rise and cool air to sink, blowing across land. The air near ground spins if there are enough sinking and rising gusts.
The tornado turns darker once it is vertical. It picks up any dust, debris, or other obstructions that get in its path. A strong tornado can even pick up houses, animals, and cars.
Why is it so difficult to predict tornadoes?
The US considers spring tornado season, but it can strike at anytime, as in the December 2021.
They are also difficult to predict, as they are smaller than other extreme weather events. They are therefore difficult to observe.
“If we think about all the different hazards we have like hurricanes, droughts, floods, tornadoes might be one of the smallest,” says Ashley, “even the most violent tornadoes are, at most, a half-mile (800 meters) wide — they occur typically in the order of seconds to minutes.”
Therefore, tornadoes are often found below certain levels that meteorologists use for modeling, observing and predicting weather events. Ashley states that scientists can simulate tornadoes using computers but that it requires a tremendous amount of computing power.
It is important to be able predict extreme weather events so authorities can issue warnings and give people the chance to escape to safety. What can they do to prepare?
Scientists monitor supercell thunderstorms for warnings and use radar technology, which measures the speed at which the mesocyclone rotates, to issue them. It is more likely to become a tornado if it rotates faster and is closer to the ground.
“The majority of the tornadoes and storms are not severe.” [we observe]”We are on the cusp. It’s almost like a storm is moving like crazy in the midlevels. But, just because it’s rotating high doesn’t necessarily indicate it’s going towards the ground,” Ashley states.
Ashley states that researchers “don’t have very accurate observations at the lowest levels of atmosphere,” and that is a crucial piece of the puzzle.
What does climate change mean for tornadoes?
The role of climate in tornadoes is complicated. Ashley insists that it is not a matter of whether climate change causes tornadoes. The question is whether or not climate change has contributed to the exact “ingredients”, which are necessary for tornadoes form.
“As it pertains to climate change, some of the essential ingredients that make up the process are known. [contribute to]Ashley says severe thunderstorms can also produce hail and tornadoes, which is increasing.”
This is evident from modeling, which shows that it is true in the United States. However, it may also be true in Europe and the UK.
Edited By: Zulfikar Abany
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
Social distancing impossible during Cyclone Amphan
As one of Bangladesh’s strongest cyclones strikes, residents are being evacuated from the coast of Bangladesh. Millions of people had been evacuated from low-lying areas of the Bay of Bengal on May 19. The coronavirus precautions make it difficult to plan. Social distancing can be nearly impossible.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
Typhoon season in the COVID-19 pandemic
Typhoon Vongfong hit the Philippines on May 14th with strong winds and heavy rainfalls. It decimated San Policarpo in Samar’s eastern province. Five people were killed and over 91,000 people were forced from their homes. Typhoons in the Philippines are not unusual at this time of the year. However, the COVID-19 emergency lockdown measures are only adding to the problems.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons, Cyclones – The power of devastation
Three names, one phenomenon
The same phenomenon is also known by the names hurricane, typhoon and cyclone. They are called hurricanes along the North American coast, while typhoons are used in East and Southeast Asia. Cyclones, which are located near India or Australia, are used to describe them. Despite their different names, they all develop in the same manner.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
A cyclone has been created
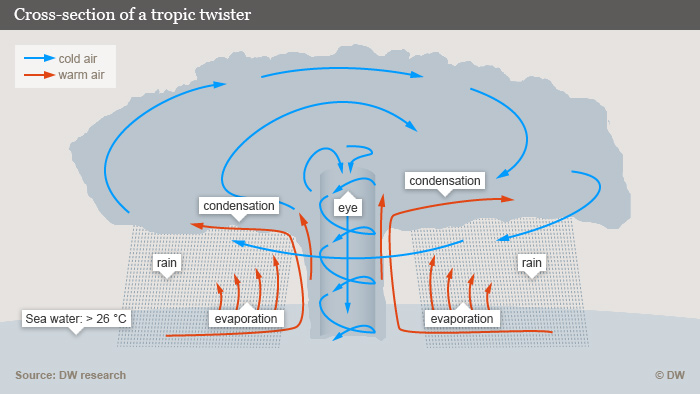
At least 26 degrees Celsius (79 degree Fahrenheit) is the minimum temperature for tropical storms to form over oceans. The warm water condenses and evaporates. The air around it heats up and pulls the cooler air upwards, creating powerful winds.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
The eye of storm
The Earth’s orbit causes the air stream around the eye to the storm to move. This can reach up to 50 kilometers in size. This area is almost entirely free from wind and clouds.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
A storm envelops the land
A tropical storm is weaker when it hits a coastline because there isn’t enough warm water. “Marcia”, a category one storm in Australia, was quickly downgraded by “Lam,” which struck near Brisbane. The worst damage is often caused by large amounts of water from the ocean – as shown here in China after Typhoon Nanmadol in Aug 2011.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
Chaos ensues
Hurricane Sandy was the strongest hurricane ever recorded over the Atlantic Ocean. It caused waves up 4 meters high, fires as well as power outages, and damaged dykes. Sandy arrived with winds of more than 140 km/h. New York, New Jersey and Cuba were particularly affected.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons, Cyclones – The power of devastation
Destructive vortex
Tornadoes can also occur in non-tropical whirlwinds. Local temperature variations cause warm air to move upwards, while cold air is forced down. A column of warm and moving air then rotates upwards with increasing velocity. Tornadoes can only reach a maximum of one kilometer in diameter.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
Fastest storms
As the warm air rises, it creates a funnel, which is the main characteristic of tornadoes. The funnel can carry air at speeds up to 500 km/h. Tornadoes are the fastest type of weather phenomenon.
-
Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones – the power to devastate
Trail of destruction
A tornado can leave a trail spanning several kilometers of destruction. Tornadoes can occur in the US Midwest several hundred times per year. This is because dry, cold air from North meets damp, warm Gulf of Mexico air. It can be different in other countries. In Germany, for instance, tornadoes sometimes occur along the coast.
Author: Brigitte Osterath / ew