Wind power, along with solar power will be the main pillar of the global renewable energy supply.
Wind power is not only carbon-neutral but can also be used to make hydrogen and other synthetic fuels in a climate-friendly manner.
Wind, like the sun, is so abundant that it could supply the entire global energy need a few times. This is crucial for the energy transformation.
But what about the negatives of wind turbines? How much wind turbines can be recycled? What about the impact on wildlife, especially birds? What is the lifetime carbon impact of wind power?
Wind’s footprint – It’s all relative
Wind turbine construction is an energy-intensive task, especially for the steel towers and concrete foundations.
According to the German Environment Agency (Umweltbundesamt UBA), it takes wind power plants between 2.5 and 11 months for them to produce the energy required for their construction.
Wind turbines can be operated for approximately 25 years on average. They generate 40 times as much energy during this time than the energy required to produce, operate, and dispose of wind power plants.
The total carbon balance of a windturbine’s lifecycle includes so-called upstream emissions. These are mostly from the production carbon-intensive steel and cement.
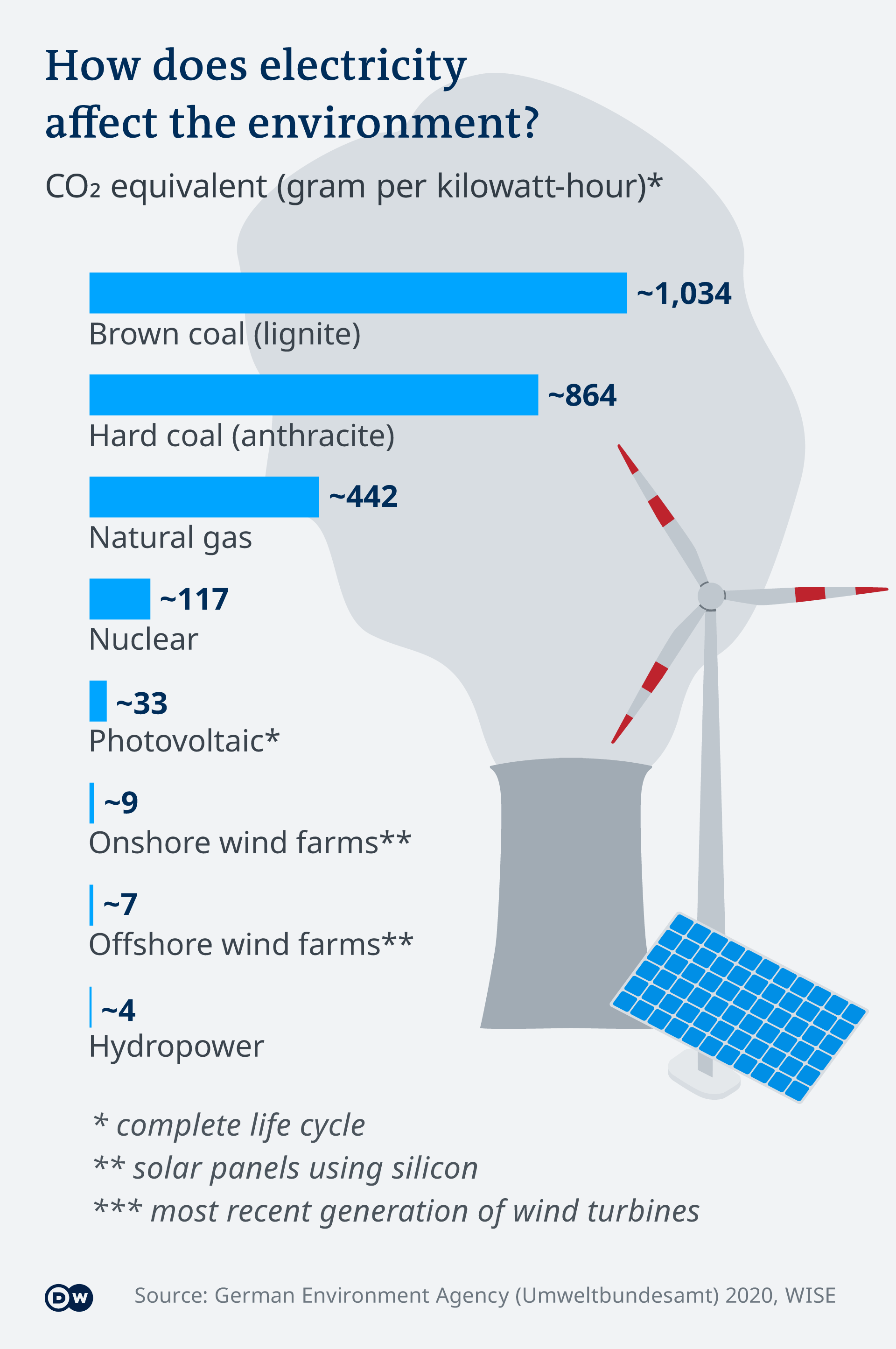
According to the UBA, an onshore wind turbine is currently being built and produces nine grams of CO2 per kilowatt hour (kWh). A new offshore wind plant in the ocean emits seven grams per kWh.
Wind power emits less carbon than other technologies. Solar power plants, on the other hand, emit 33 grams CO2 per kWh. For comparison, power from natural gas produces 442g CO2 per kWh, while power from hard coal emits 864g and power from brown coal emits 1034g.
According to A studyWISE, a global anti-nuclear group, commissioned this study. Nuclear energy accounts for about 112 grams of CO2 per kWh. This is despite the fact that uranium mining, construction, and operation of nuclear reactors, are both major sources of emissions.
-
The fascination with wind power
Windsurfing: The way to victory
Windsurfers can now glide over water at speeds exceeding 90 km/h. This requires skill, technique, great equipment, and lots of wind. Kiran Badloe, a Dutch windsurfer, wins the gold medal at the Tokyo Olympics.
-
The fascination with wind power
Skiing with a sail
The conditions for snowkiting, also known as kite ski, are ideal in Russia’s Novosibirsk. The cold winters are a great place to snowkite, as there are large areas of frozen ground and strong winds. The stunt kite can reach speeds of over 110 km/h.
-
The fascination with wind power
Maximum speed of 200 km/h
Land sailing, also known by sand yachting is done in another wind-powered vehicle. It can go very fast. Richard Jenkins, a landsailer, reached 203 km/h in Salt Lake, Nevada in 2009. Precursors were believed to have existed in the windy north China in the 6th Century and in Europe in the 17th Century.
-
The fascination with wind power
Carbon-free travel
Greta Thunberg raced the emissions-free racing yacht Malizia across the Atlantic in 2019. The journey of more than 5,300 km from Plymouth, England to New York took Thunberg, then 16, 14 days. This was a pioneering example of CO2-free travel, according to the climate activist. With the help of solar panels and underwater turbines, electrical energy is generated aboard the “Malizia”.
-
Wind power: The fascination
Don Quixote’s battle against windmills
There were hundreds of such mills in Spain during the 16th century, in windy Castilla La Mancha. The blades were covered with canvas to make a sail that could be propelled by wind. These Spanish windmills were famously shown in Don Quixote’s novel. The title character, who is confused about his identity, fights with the towers he thinks are giants.
-
Wind power: The fascination
Wind waterpumps
These windmills in Rotterdam, Netherlands, are masterpieces of engineering dating back to the 18th century. The wind-powered devices were built to pump water from low-lying areas. The resulting swamp could be used to grow crops, allowing for greater prosperity in the area. Today, the wind pumps are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
-
The fascination with wind power
Fascinated and fascinated by wind technology
Modern power generation with wind started in 1980 in Palm Springs, California. There, thousands of three-blade blade turbines were built. Today, these oldest turbines are a tourist attraction. Their output of 25 kilowatts is far less than modern turbines that produce 500 times as much. Denmark and Germany were also leaders in modern wind technology, particularly with offshore wind.
-
The fascination with wind power
Joy over progress
Two headdressed women take a selfie in front a modern wind turbine in Rong’an County in China. China has been a pioneer in wind power development in recent years. In 2020, 53 gigawatts of turbines were installed. This is equivalent to 53 nuclear power plants’ annual output.
-
The fascination with wind power
The future is your model
Floating wind technology is the subject of much research. This model turbine, which has two rotors, is 18 meters tall and is currently being tested in Baltic Sea. The actual working turbine will stand 180 meters high and produce 15,000 kilowatts. EnBW, the German energy company, has invested heavily in the turbines. In 2022, the first large-scale turbine offshore of China will be tested.
-
The fascination with wind power
Stunt kite makes electricity
Stunt kites are capable of pulling athletes and ships. This one from northern Germany generates electricity. During the climb, the rope pulls on an electric generator-powered winch. Once at the top, it is turned out by the wind and brought back with less power, starting a new cycle of power generation. The technology is being developed in collaboration with RWE, Europe’s largest coal company.
-
The fascination with wind power
Ende und Aufbruch
Germany’s new coalition has made a commitment to eliminate coal power by 2030. Wind-generated electricity will soon be the largest source of power, along with solar. This trend will continue in other countries.
Author: Gero Rueter
What can be reused?
In the past 30 years, wind power has grown exponentially. Germany had 50 wind turbines that could generate 100 kilowatts of power in 1991. 2001 saw the addition 2000 more turbines with a power output of 1300 kilowatts to the grid.
These small-scale plants can be maintained well and can last more than 30 years. They can now be found all over the world.
Only a few old plants have been taken down or deconstructed due to their long lifespan. However, wind power technology will be replacing up to 50,000 plants by 2050.
This will involve the removal of large amounts of concrete, steel in tower and gear box, and a mixture of plastic with glass-or carbon fiber used for the rotor blades.
Concrete can be crushed into road blocks. The precious steel can also be recycled to make new steel. Other valuable metals, such as copper and aluminum, can also be recycled.
Recycling rotor blades made out of plastic composites is difficult. In the US, there are no old rotorblades. End up in disposal sites. They have been used mainly in Europe as an alternate fuel in cement incinerators and cement kilns.
Denmark is currently producing the first recyclable rotorblades for large offshore plants. Siemens Gamesa, the plant builder, plans to only sell recyclable blades from 2030. The company’s wind power plants will also be completely carbon neutral by 2040.
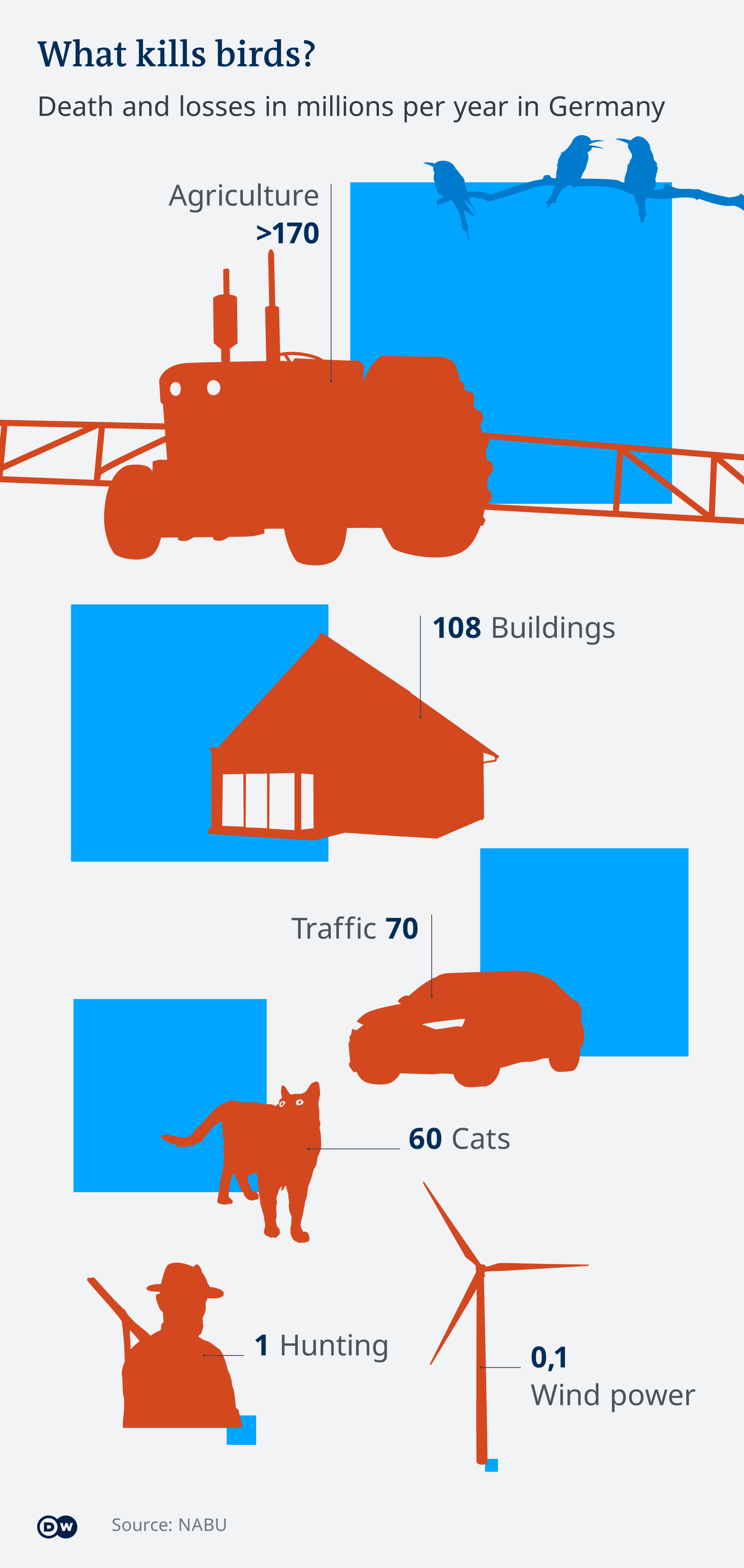
Is wind power a good option for species protection?
A rapid expansion of wind power will reduce CO2 emissions and help to slow global warming.
However, environmentalists insist that wind power plants should not be placed in natural reserves or at migratory bird stopover locations in order to not endanger wildlife.
An increasing number of large-scale wind energy plants are equipped with software and cameras that can detect birds and switch off turbines to reduce the risk of collisions.
The foundations for offshore winds plants were also built on the seabed, causing disturbances to fish, whales, and seals.
This problem was solved technicaly by a ring of small air bubbles, which are used during construction activities to dampen noise by around 90%.
Even offshore wind plants can have a positive impact on sea animals, since the area is no longer used for trawl fishing. This allows fish stocks to recover. Additionally, sea crea colonizes the plants’ foundations.
Moussels are another example of tures.
Global warming causing less wind?
Although warm summers are often dry and windless, there are many stormy places in the colder months or during winter.
But this doesn’t mean that wind power will be affected by climate change. Research shows that rising temperatures will not affect wind power in any significant way. Global wind power is lower.
Global warming slows down the jet stream that is located eight to twelve km above sea level. However, this does little to affect the year-round energy yield from wind power plants.
The wind capacity will eventually be balanced by rising temperatures. Future winters are expected to be more windy, but summers will be cooler.
-
The future of wind power
Now and then
For centuries, wind power has been used. It pumps water and grinds grain to make sailboats. There were hundreds of thousands wind turbines across Europe in the 19th Century. The Dutch used them mainly to drain marshes. Wind power generates clean electricity today and is crucial to meeting climate goals.
-
The future of wind power
Wind beats coal
Wind turbines are known for producing the cheapest electricity. Today, electricity generated from new coal or nuclear power plants costs two to three-times more. Wind power produced on land is especially cheap. Forecasts predict that wind power costs will drop to 0.03$0.04 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) by 2030 in good winds locations.
-
The future of wind power
20 times more electricity
A large wind turbine located near Wilhelmshaven, northern Germany, generates 6,000 kilowatts and provides enough electricity for 10,000 households. Older models, dating back 25 years ago, only produced 500 kilowatts sufficient to power approximately 500 people. Modern turbines reach 180 meters into the air. The higher they are, the more wind they capture.
-
The future of wind power
Giants at sea
Wind is strong and reliable at sea. Offshore parks like this one off of the Dutch coast account about 5% worldwide’s wind power. These turbines can produce up to 10,000 kilowatts. Their output is expected to increase to as high as 15,000 kilowatts in 2025, and provide electricity for more people than 40,000.
-
The future of wind power
China leads the charge
China is home to half of all new wind farms worldwide. China built 52 gigawatts of new wind power turbines in 2020. This is equivalent to 50 nuclear power stations. Germany and Denmark are the leaders in wind expansion. Denmark covers approximately 50% of its electricity needs using wind power, while Germany only manages 25%.
-
The future of wind power
More jobs with wind power
Around 1.3 million people work within the wind industry in all parts of the world. Around 550,000 are located in China, 110,000 in America, 90,000 in Germany and 45,000 in India. There are also 40,000 in Brazil. Wind turbines are more expensive than coal-fired power so more people are looking for work.
-
The future of wind power
Citizens want to make money
Wind power is often opposed by residents in densely populated areas. This can change if citizens become involved in local projects. Many residents in Starkenburg, Germany, are supportive of the expansion of wind power. They invest in new turbines and make money from the sale of electricity.
-
The future of wind power
Sails save diesel
Sailing ships used to transport freight around the globe, but diesel engines replaced them. Modern sails are now back in play. Additional wind propulsion can reduce freighter energy consumption by up to 30%. Green hydrogen will also be an option for ships in the future.
-
The future of wind power
Floating wind farms
There is plenty of room in the sea to support wind power. However, the water is often too deep to support a foundation in the seabed. Floating turbines mounted on buoys offer an alternative. They are secured to the seabed by long chains. Floating wind farm systems are already in place in Japan and Europe.
-
The future of wind power
Wind power for your home
The 147-meter tall Strata SE1 skyscraper in London, England is a striking sight with its futuristic wind turbines. These rooftop installations are often not economically viable because the wind in cities tends to be too weak. Photovoltaic systems installed on roofs are almost always a better alternative.
-
The future of wind power
Most environmentally-friendly energy
Wind turbines produce the energy they need within three to eleven months. While they don’t emit any CO2, the electricity generation process does alter the landscape. They are still better than other energy sources in terms of the environmental balance sheet. According to Germany’s Federal Environment Agency, their environmental costs are 70 times lower that those of coal-fired power.
-
The future of wind power
Where can you put wind power?
Combining solar power plants and wind can provide the world with energy. Wind turbines produce electricity at winds speeds of 10 km/h or more. Photovoltaics is the most cost-effective energy source in regions with lots of sun. It is often a mixture of solar and wind power, a little further north and south than the Equator. Wind power can be the main source of energy in windy regions.
Author: Gero Rueter